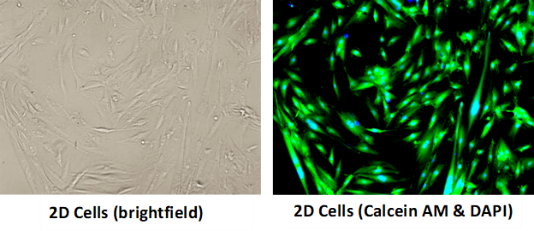
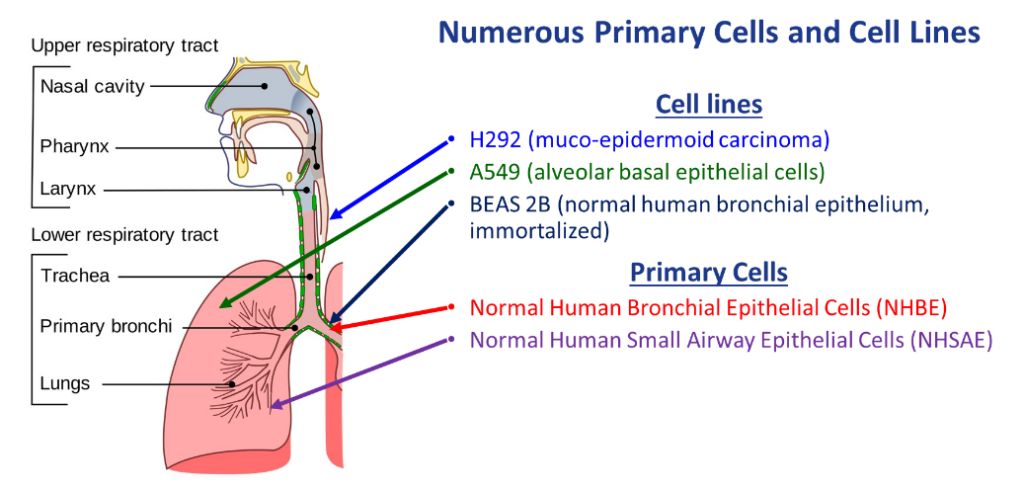
Pulmonary cell lines are readily available that are derived from lung tissue. Screening efforts often require rapid and cost-effective throughput to prioritize products in development. Cell lines such as BEAS-2B, A549, and H292 are commonly employed as a means to make basic determinations of cytotoxicity and viability following test material exposure. Reporter cell lines (not necessarily of pulmonary origin) can answer more specific questions about effects of materials on cells, such as oxidative stress (Nrf2/ARE) and the activation of inflammatory pathways (NFκβ). These can also be multiplexed with other endpoints to maximize return. Cell lines are an efficient and cost-effective option when screening large numbers of materials.
2D Cell Lines and Primary Cells
Respiratory Toxicity Screening Services
For rapid and cost-effective evaluation of compounds and formulations, IIVS offers analysis of test materials in the cells lines described above. Cytotoxicity markers (e.g. LDH leakage and WST-8 reduction) can be combined with additional endpoints such as inflammation and oxidative stress to determine whether additional evaluation of the test material is needed. Contact us at clientservices@iivs.org for further information.